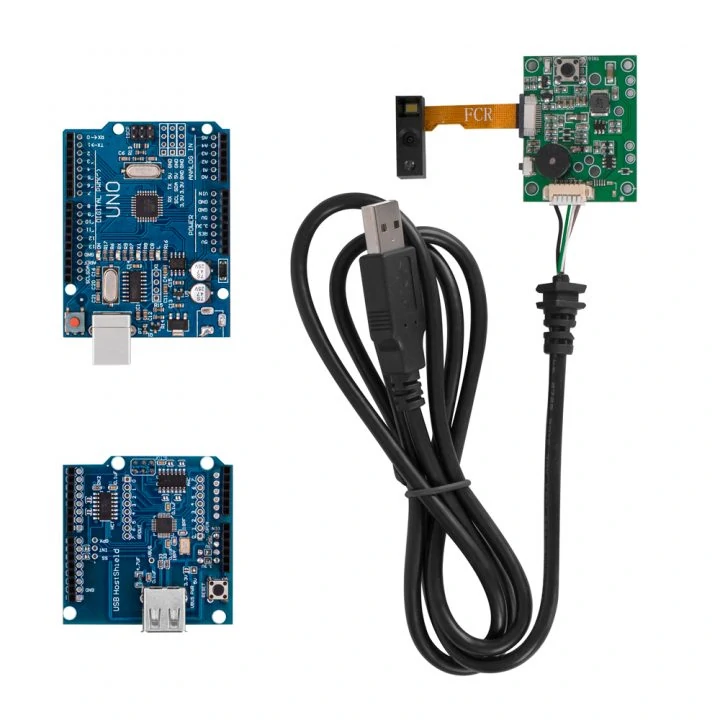
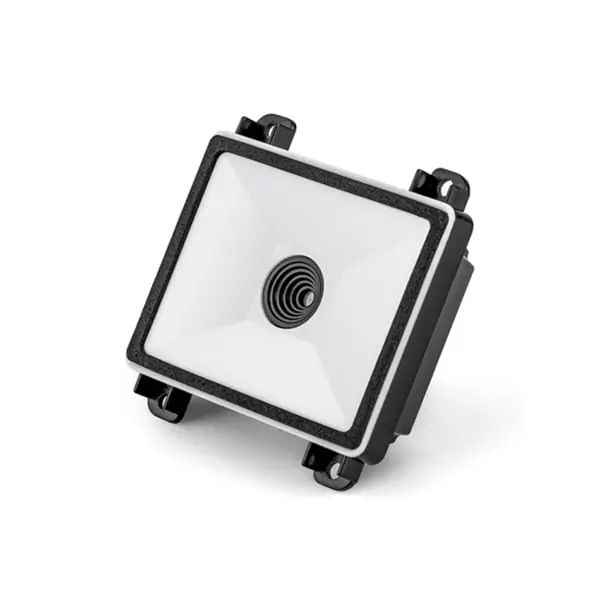
Arduino barcode scanner: connect OEM barcode scanners modules with Arduino microcontroller (MCU)
If you are using an Arduino microcontroller to develop your system, and you need a 1d/ 2d OEM barcode scanner module at the same time, then this article would be helpful for you:
Here we introduce how we connect the Arduino Uno microcontroller with RTscan OEM barcode scanner modules and make them work.
When we try to integrate an OEM barcode scanner with the Arduino microcontroller board, we would meet these problems:
- The OEM barcode scanner with 12pins TTL interface, but Arduino board without this connector, how can we connect them?
- Whatever OEM barcode scanners we choose, how can we control the barcode scanner by Arduino and also upload decoded data to the Ardunio system?
Read below and find how RTscan provides solutions for the above questions.
Part I: Introduction of Arduino UNO and RTscan barcode scanners
Arduino UNO:
The UNO is the most used and documented board of the whole Arduino microcontrollers family, many people choose this model for their projects. Arduino Uno has 14 digital input/output pins (of which 6 can be used as PWM outputs), 6 analog inputs, a 16 MHz quartz crystal, a USB connection, a power jack, and ICSP header, and a reset button. It contains everything needed to support the microcontroller.
Arduino UNO Pinout
And for our application to connect with the OEM barcode scanner, we need the 5.0v power supply pin, and GND pin, RXD, TXD pins.
RTscan OEM barcode scanners:
They all with 12pins connector and TTL signal, and use FFC cable and connector like this :

In this article, we choose RT214 as an example to do the connection and integration.
Part II: Connection solutions:
RTscan provides two types of solutions:
Solution 1: UART TTL Interface
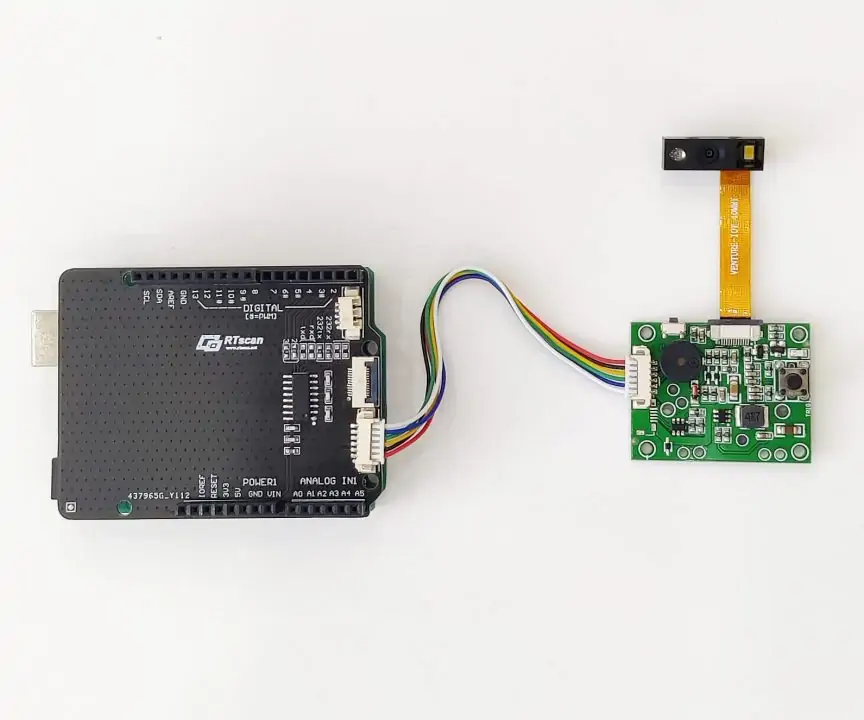
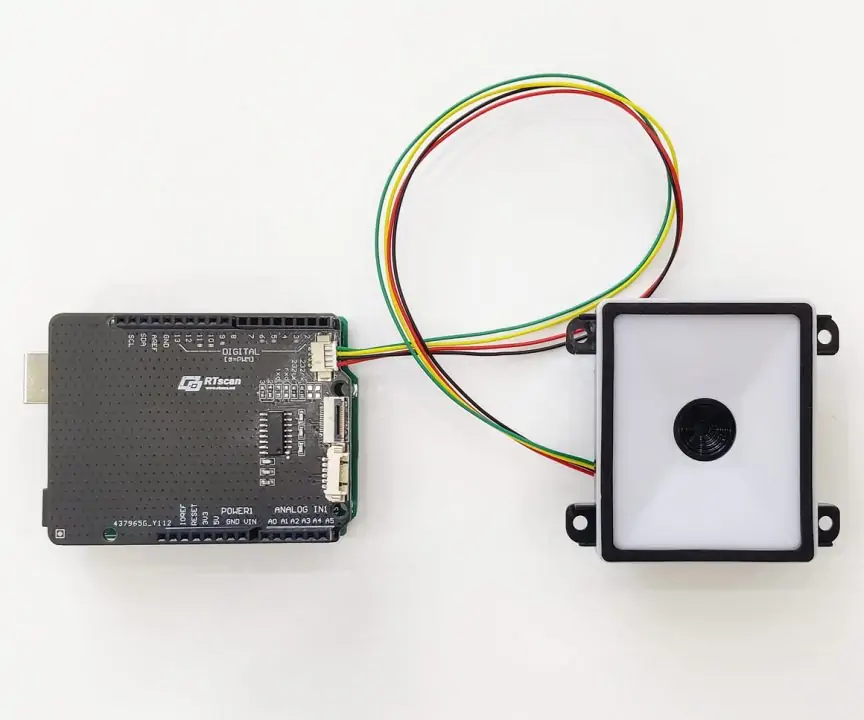
RTscan developed a multi-interface Shield, connect the shield with Arduino UNO, connect the OEM barcode scanners to our EVK board (with trigger button and beeper ), then connect them via a 6pins UART TTL cable:
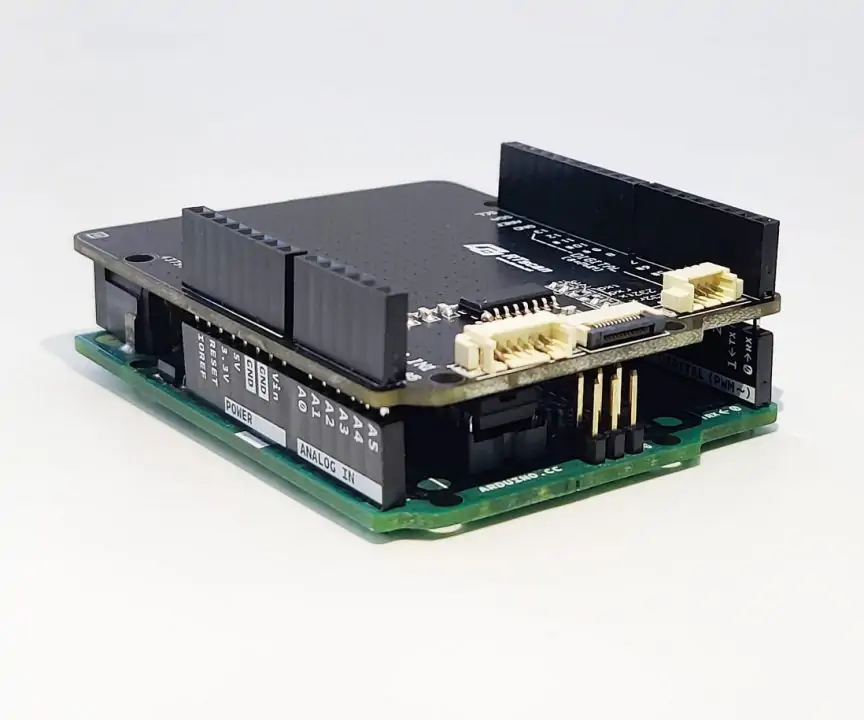

Via this solution, we make the connection between the barcode scanner engine and Arduino much durable/ solid.
And for this solution, the RT214 scanner needs to be set to TTL-232 Communication (follow Part III/TTL-232 communication).
♠ OEM Scanner Modules that compliant with this solution:
| RT217 | RT206 | RT207 | RT208 | RT214 | RT214B | RT214C |
|---|
∗please click the model number to view the full product introduction page.
Note: we have similar solutions for fixed mount type scanner RT830C and RT830i
UART-TTL:
12pins flat cable TTL-232:
If you prefer this type of scanner, please contact our sales team to get detailed information: sales@rtscan.net
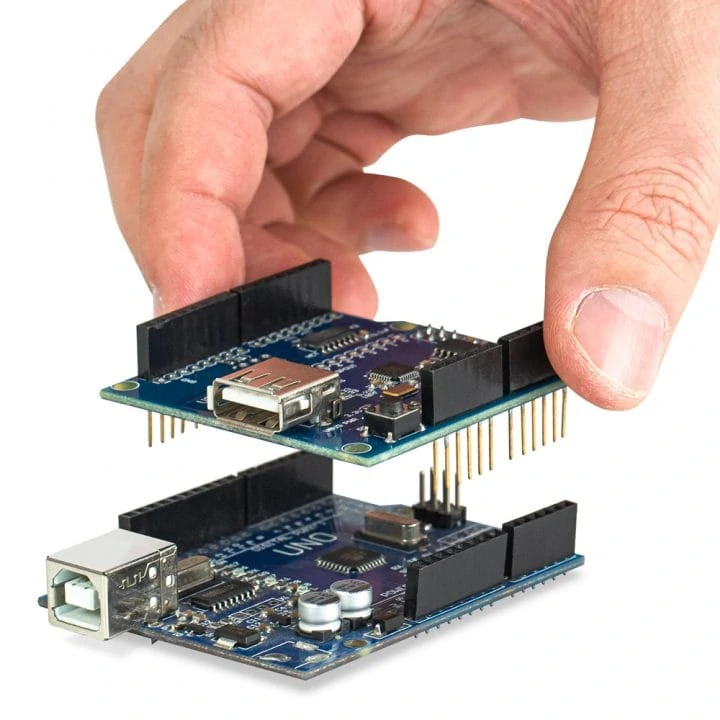
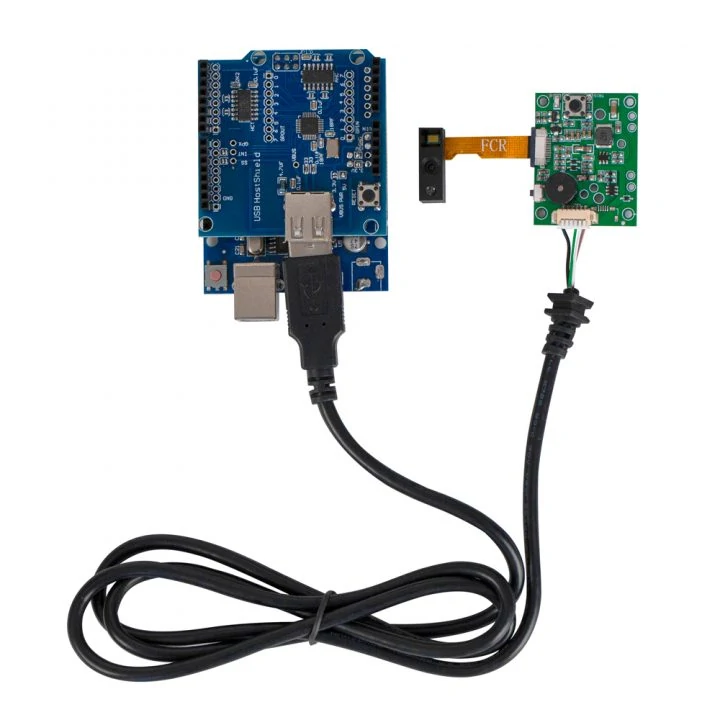
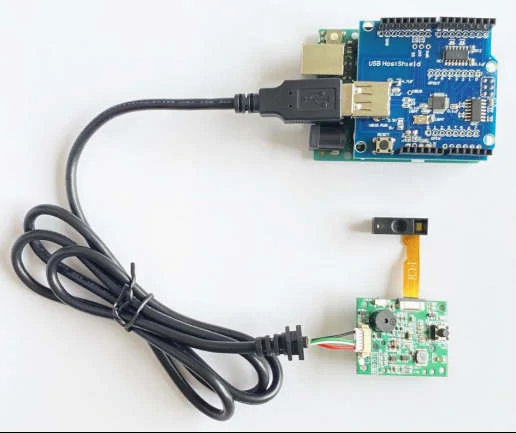
Solution 2: Connect via USB host A
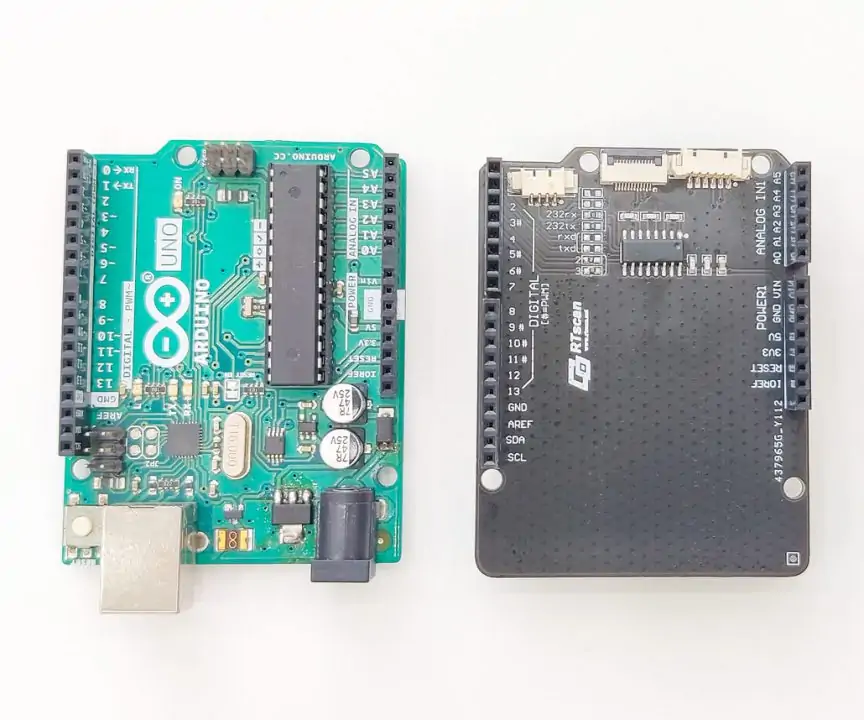
If you prefer your barcode scanner with a USB interface instead of a UART TTL cable, then you can use this solution: use an Arduino USB host shield.
The Arduino USB Host Shield allows you to connect a USB barcode scanner to your Arduino board, set up RTscan’s barcode scanner to HID mode, or USB CDC (Virtual Com mode).
Please follow Part III/USB CDC Communication/USB-HID Communication to check how to make them work together.
♠ Barcode Scanner Modules that compliant with this solution:
All barcode scanners have a USB interface. All RTscan’s OEM scanner modules, fixed-mount types, and handheld types.
Part III:
Get the OEM barcode scanner module work with the Arduino system /Arduino C++ sample code:
We developed sample code (only compatible with RTscan’s scanners) to work with our scanners so that you can copy our source codes and program your system very quickly and no need to write the whole code one by one; save your time and speed up your integration work!
In this article, we choose RT214 as an example to do the programming.
1. UART-TTL Communication
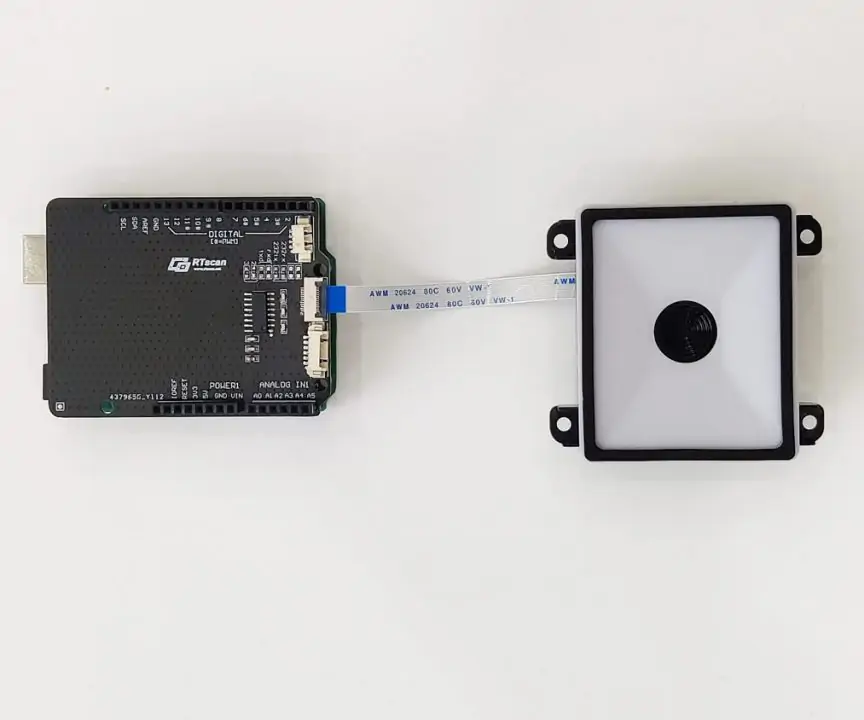
Step 1: Hardware connection
Connect RT214+EVK board to Arduino UNO as said above
Step 2: RT214 settings
RT214 needs to be set up with TTL-232 mode, scan the following barcode
Set to TTL-232 Mode, the default baud rate is 9600, 8-n-1
Enter setup
Set to TTL-232 mode
For more details, please refer to «RT214_User_Guide»
Step 3: Run the sample code
Upload the below sample code rt214_test_demo.ino to Arduino UNO.
/*
# RT214/RT212 Command Syntax
#
# Prefix Storage Tag SubTag {Data} [, SubTag {Data}] [; Tag SubTag {Data}] […] ;
# Suffix Among which, {data} means integrant while [data] means optional data.
#
# Prefix: “~<SOH>0000” (HEX: 7E 01 30 30 30 30), 6 characters.
# StorageType:
# “@” or “#”,1 character.
# “@” means permanent setting which will not be lost by removing power from the scanner or rebooting it;
# “#” means temporary setting which will be lost by removing power from the scanner or rebooting it.
# Tag:
# A 3-character case-sensitive field that identifies the desired command group.
# For example, the Tag for the Enable Code 11 is C11 (see Example 1 of Chapter 1).
# SubTag:
# A 3-character case-sensitive field that identifies the desired parameter within the tag group.
# For example, the SubTag for the Enable Code 11 is ENA (see Example 1 of Chapter 1).
# Data:
# The value for a feature or parameter setting, identified by the Tag and SubTag.
# For example, the Data for the Enable Code 11 is 1 (see Example 1 of Chapter 1).
# Suffix:
# “;<ETX>” (HEX: 3B 03), 2 characters.
*/
void send_cmd(char * StorageType_Tag)
{
const char *Prefix = "\x7E\x01\x30\x30\x30\x30";
const char *Suffix = "\x3B\x03";
mySerial.print(Prefix);
mySerial.print(StorageType_Tag);
mySerial.print(Suffix);
Serial.print("Send Command:");
printHex(Prefix, strlen(Prefix));
printHex(StorageType_Tag, strlen(StorageType_Tag));
printHex(Suffix, strlen(Suffix));
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Command response:");
read_response(50);
Serial.println();
}
void read_response(unsigned long timeout)
{
unsigned long t = millis();
unsigned char c;
while (millis() - t < timeout)
{
if (mySerial.available() > 0)
{
c = mySerial.read();
printHex((char *)&c, 1);
}
}
}
void start_scanning()
{
Serial.println("start scanning");
send_cmd("#SCNTRG1");
}
void stop_scanning()
{
Serial.println("stop scanning");
send_cmd("#SCNTRG0");
}
Please contact us to get full sample codes: sales@rtscan.net
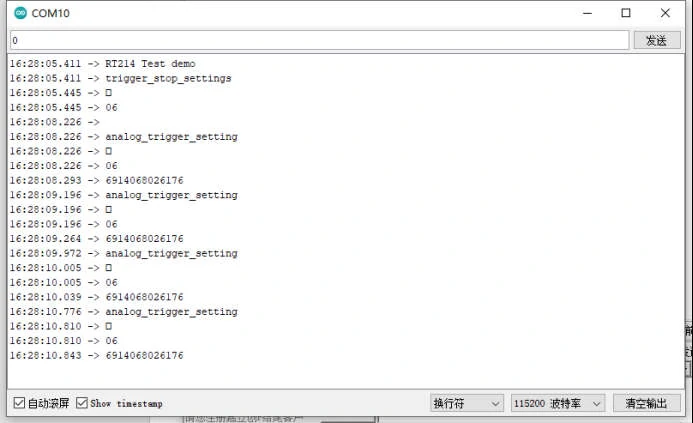
And the RT214 automatically detects and reads bar codes.
Output:
Introduction of the serial port commands protocol for RT214
The often-used serial port commands are as below (HEX):
Trigger mode:1B 31
Stop scanning:1B 30
Auto mode:1B 32
Continuous read mode:1B 33
For more details, please refer to 《RTscan Serial Programming Command Manual.PDF》
2. USB CDC Communication
In this solution, we connect the OEM barcode scanner to Arduino via USB host shield, and firstly we need to set the scanner to USB Virtual Com emulation mode, and the Arduino recognizes the scanner as a USB CDC device. Follow the steps as below:
Step 1: Hardware connection
Connect the RT214 scanner to the USB port of the Arduino USB host shield through a USB data cable.
Step 2: RT214 settings
RT214 set to USB CDC mode, scan the following Setting bar code.
Enter setup
Set to USB-CDC mode:
Recognized as a COM port device on the computer:
Step 3: Include the library
Arduino Library Manager
First, install Arduino IDE version 1.6.2 or newer, then simply use the Arduino Library Manager to install the library.
Please see the following page for instructions:
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Guide/Libraries#toc3
Manual installation
First download the library by clicking on the following link:
https://github.com/felis/USB_Host_Shield_2.0
Then uncompress the zip folder and rename the directory to «USB_Host_Shield_20», as any special characters are not supported by the Arduino IDE.
Now open up the Arduino IDE and open «File>Preferences». There you will see the location of your sketchbook. Open that directory and create a directory called «libraries» inside that directory. Now move the «USB_Host_Shield_20» directory to the «libraries» directory.
The final structure should look like this:
- Arduino/
- libraries/
- USB_Host_Shield_20/
- libraries/
Now quit the Arduino IDE and reopen it.
Now you should be able to open all the examples codes by navigating to «File>Examples>USB_Host_Shield_20» and then select the example you will like to open.
For more information please visit the following sites:
http://arduino.cc/en/Guide/Libraries
https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-all-about-arduino-libraries-install-use.
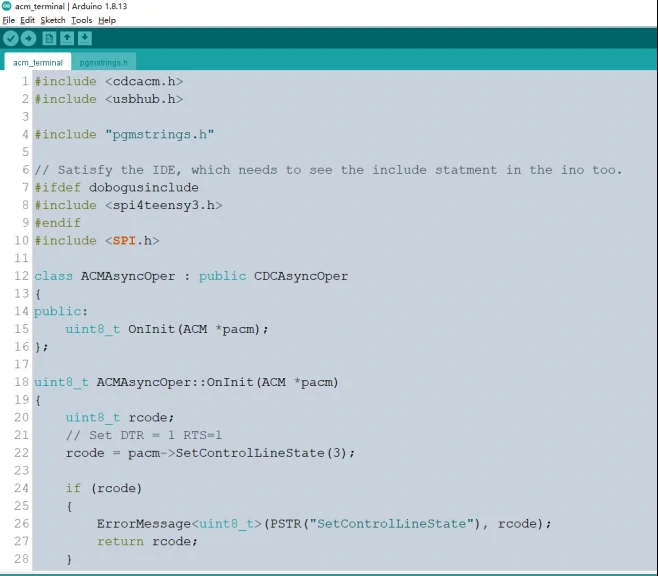
Step 4: Run the sample code
Run:
acm_terminal. ino
#include <cdcacm.h>
#include <usbhub.h>
#include "pgmstrings.h"
// Satisfy the IDE, which needs to see the include statment in the ino too.
#ifdef dobogusinclude
#include <spi4teensy3.h>
#endif
#include <SPI.h>
class ACMAsyncOper : public CDCAsyncOper
{
public:
uint8_t OnInit(ACM *pacm);
};
uint8_t ACMAsyncOper::OnInit(ACM *pacm)
{
uint8_t rcode;
// Set DTR = 1 RTS=1
rcode = pacm->SetControlLineState(3);
if (rcode)
{
ErrorMessage<uint8_t>(PSTR("SetControlLineState"), rcode);
return rcode;
}
LINE_CODING lc;
lc.dwDTERate = 115200;
lc.bCharFormat = 0;
lc.bParityType = 0;
lc.bDataBits = 8;
rcode = pacm->SetLineCoding(&lc);
if (rcode)
ErrorMessage<uint8_t>(PSTR("SetLineCoding"), rcode);
return rcode;
}
USB Usb;
//USBHub Hub(&Usb);
ACMAsyncOper AsyncOper;
ACM Acm(&Usb, &AsyncOper);
void setup()
{
Serial.begin( 115200 );
#if !defined(__MIPSEL__)
while (!Serial); // Wait for serial port to connect - used on Leonardo, Teensy and other boards with built-in USB CDC serial connection
#endif
Serial.println("Start");
Serial.println("Please set the scanner to USB CDC mode");
if (Usb.Init() == -1)
Serial.println("OSCOKIRQ failed to assert");
delay( 200 );
}
void loop()
{
...
Please contact us to get full sample codes: sales@rtscan.net
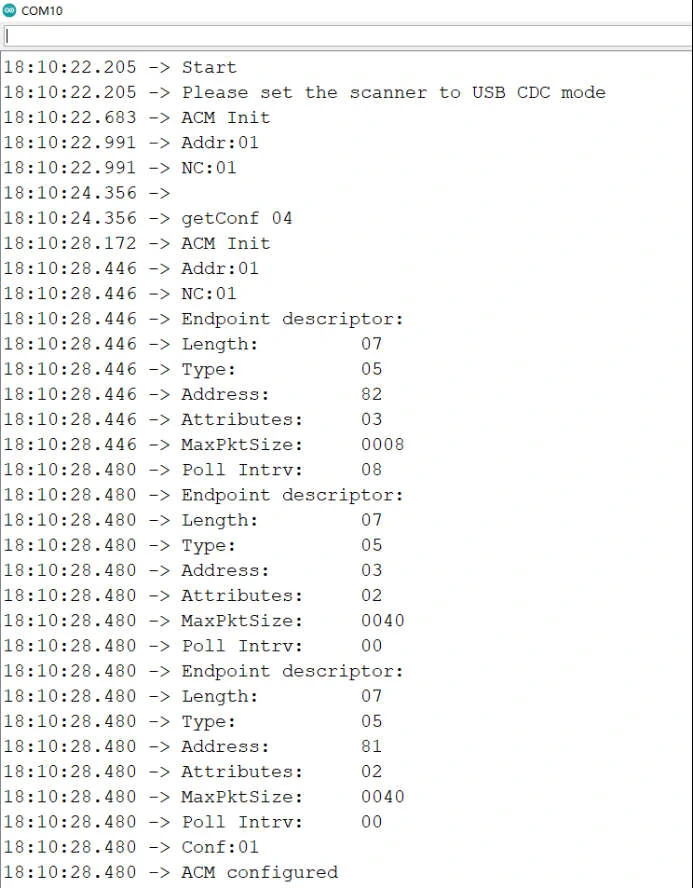
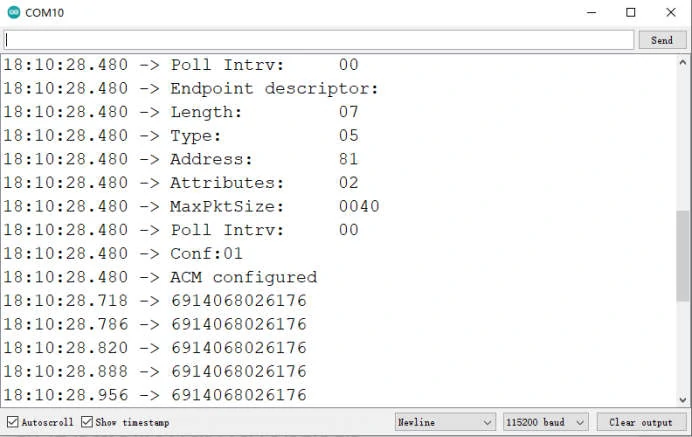
Open the serial port for debugging:
Scan any barcode and it will be shown as below:
3. USB-HID Communication
In this solution, the scanner is set to USB HID KBW mode, and the Arduino recognizes the scanner as a USB keyboard simulation device.
Step 1: Hardware connection
Connect the RT214 scanner to the USB port of the Arduino USB host shield through a USB data cable.
Step 2: RT214 settings
RT214 set to USB CDC mode, scan the following Setting bar code
Enter setup:
Set to USB-HID mode:
Recognized as on the computer:
Step 3: Include the library
Arduino Library Manager
First, install Arduino IDE version 1.6.2 or newer, then simply use the Arduino Library Manager to install the library.
Please see the following page for instructions:
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Guide/Libraries#toc3
Manual installation
First download the library by clicking on the following link:
https://github.com/felis/USB_Host_Shield_2.0
Then uncompress the zip folder and rename the directory to «USB_Host_Shield_20», as any special characters are not supported by the Arduino IDE.
Now open up the Arduino IDE and open «File>Preferences». There you will see the location of your sketchbook. Open that directory and create a directory called «libraries» inside that directory. Now move the «USB_Host_Shield_20» directory to the «libraries» directory.
The final structure should look like this:
- Arduino/
- libraries/
- USB_Host_Shield_20/
- libraries/
Now quit the Arduino IDE and reopen it.
Now you should be able to open all the examples codes by navigating to «File>Examples>USB_Host_Shield_20» and then selecting the example you would like to open.
For more information please visit the following sites:
http://arduino.cc/en/Guide/Libraries
https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-all-about-arduino-libraries-install-use.
Step 4: Run the sample code
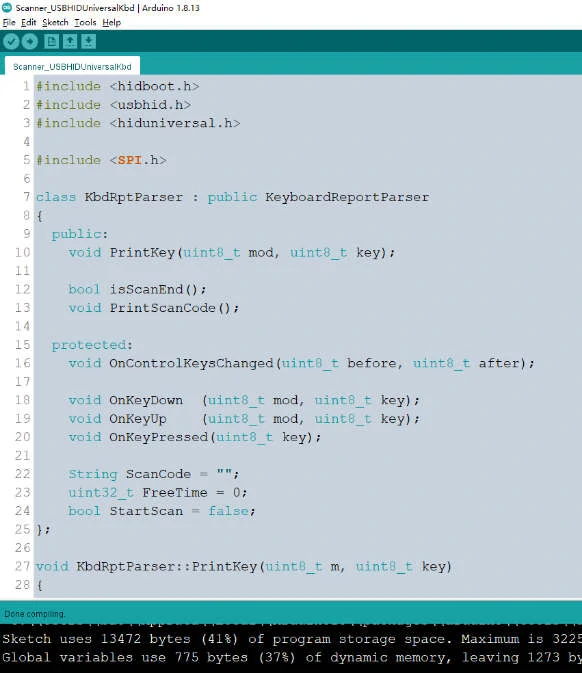
Run: Scanner_USBHIDUniversalKbd. ino
#include <hidboot.h>
#include <usbhid.h>
#include <hiduniversal.h>
#include <SPI.h>
class KbdRptParser : public KeyboardReportParser
{
public:
void PrintKey(uint8_t mod, uint8_t key);
bool isScanEnd();
void PrintScanCode();
protected:
void OnControlKeysChanged(uint8_t before, uint8_t after);
void OnKeyDown (uint8_t mod, uint8_t key);
void OnKeyUp (uint8_t mod, uint8_t key);
void OnKeyPressed(uint8_t key);
String ScanCode = "";
uint32_t FreeTime = 0;
bool StartScan = false;
};
void KbdRptParser::PrintKey(uint8_t m, uint8_t key)
{
MODIFIERKEYS mod;
*((uint8_t*)&mod) = m;
Serial.print((mod.bmLeftCtrl == 1) ? "C" : " ");
Serial.print((mod.bmLeftShift == 1) ? "S" : " ");
Serial.print((mod.bmLeftAlt == 1) ? "A" : " ");
Serial.print((mod.bmLeftGUI == 1) ? "G" : " ");
Serial.print(" >");
PrintHex<uint8_t>(key, 0x80);
Serial.print("< ");
Serial.print((mod.bmRightCtrl == 1) ? "C" : " ");
Serial.print((mod.bmRightShift == 1) ? "S" : " ");
Serial.print((mod.bmRightAlt == 1) ? "A" : " ");
Serial.println((mod.bmRightGUI == 1) ? "G" : " ");
};
void KbdRptParser::OnControlKeysChanged(uint8_t before, uint8_t after) {
MODIFIERKEYS beforeMod;
*((uint8_t*)&beforeMod) = before;
MODIFIERKEYS afterMod;
*((uint8_t*)&afterMod) = after;
if (beforeMod.bmLeftCtrl != afterMod.bmLeftCtrl) {
Serial.println("LeftCtrl changed");
}
if (beforeMod.bmLeftShift != afterMod.bmLeftShift) {
Serial.println("LeftShift changed");
}
if (beforeMod.bmLeftAlt != afterMod.bmLeftAlt) {
Serial.println("LeftAlt changed");
}
if (beforeMod.bmLeftGUI != afterMod.bmLeftGUI) {
Serial.println("LeftGUI changed");
}
if (beforeMod.bmRightCtrl != afterMod.bmRightCtrl) {
Serial.println("RightCtrl changed");
}
if (beforeMod.bmRightShift != afterMod.bmRightShift) {
Serial.println("RightShift changed");
}
if (beforeMod.bmRightAlt != afterMod.bmRightAlt) {
Serial.println("RightAlt changed");
}
if (beforeMod.bmRightGUI != afterMod.bmRightGUI) {
Serial.println("RightGUI changed");
}
}
void KbdRptParser::OnKeyDown(uint8_t mod, uint8_t key)
{
// Serial.print("DN ");
// PrintKey(mod, key);
uint8_t c = OemToAscii(mod, key);
if (c)
OnKeyPressed(c);
}
void KbdRptParser::OnKeyUp(uint8_t mod, uint8_t key)
{
// Serial.print("UP ");
// PrintKey(mod, key);
FreeTime = millis();
StartScan = true;
}
void KbdRptParser::OnKeyPressed(uint8_t key)
{
// Serial.print("ASCII: ");
// Serial.println((char)key);
ScanCode = ScanCode + String((char)key);
};
bool KbdRptParser::isScanEnd()
{
if(millis() - FreeTime > 200 && StartScan){
StartScan = false;
return true;
}
return false;
};
void KbdRptParser::PrintScanCode()
{
Serial.print("ScanCode: ");
Serial.println(ScanCode);
ScanCode = "";
};
USB Usb;
HIDUniversal Hid(&Usb);
KbdRptParser Prs;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin( 115200 );
#if !defined(__MIPSEL__)
while (!Serial); // Wait for serial port to connect - used on Leonardo, Teensy and other boards with built-in USB CDC serial connection
#endif
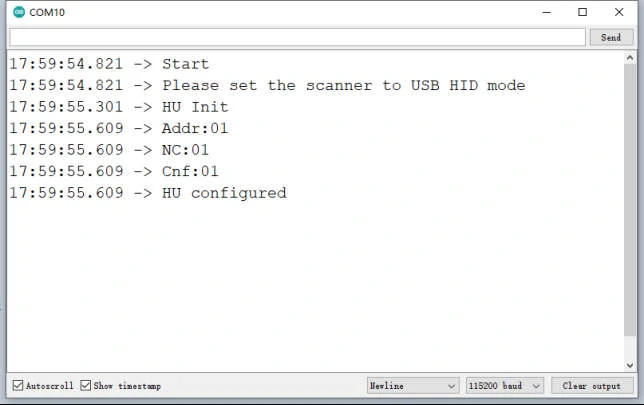
Serial.println("Start");
Serial.println("Please set the scanner to USB HID mode");
if (Usb.Init() == -1)
Serial.println("OSC did not start.");
delay( 200 );
Hid.SetReportParser(0, &Prs);
}
void loop()
{
Please contact us to get full sample codes: sales@rtscan.net
Open the serial port for debugging:
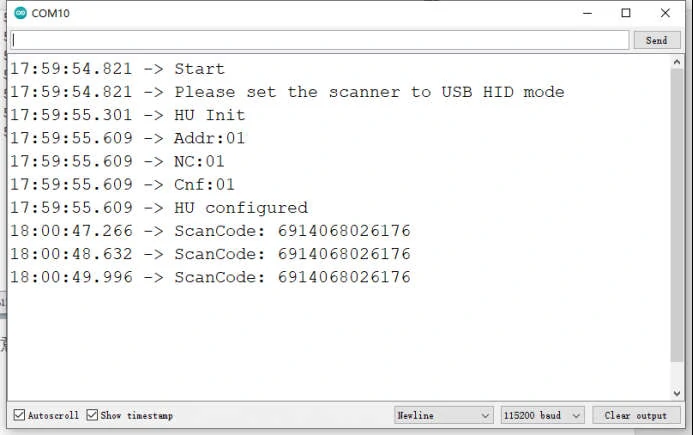
Scan any barcode and it will be shown as below:
This article is a solution introduction for Arduino barcode scanners, if you are using Raspberry Pi and need an OEM barcode scanner, please read: Raspberry Pi barcode scanner
If you need an embedded type 2d and QR barcode scanner for Arduino, please read:
Embedded QR Code scanner for Arduino
If you need an Embedded barcode scanner for Raspberry Pi, please read:
Embedded barcode scanner for Raspberry Pi
We developed an Arduino solution for most of our OEM barcode scanners, includes RT203 RT206 RT207 RT208 RT209 RT211 RT830B, if you want to learn more about them, please view below: https://www.rtscan.net/barcode-readers/oem-barcode-scanners/